Mini Gastric Bypass
Gastric bypasses are malabsorptive bariatric surgical procedures. The aim of gastric bypasses are reducing the stomach volume and separating the small intestines from absorption function. There is different kind of gastric bypasses which has been applied for decades. These are surgeries performed with laparoscopic method.
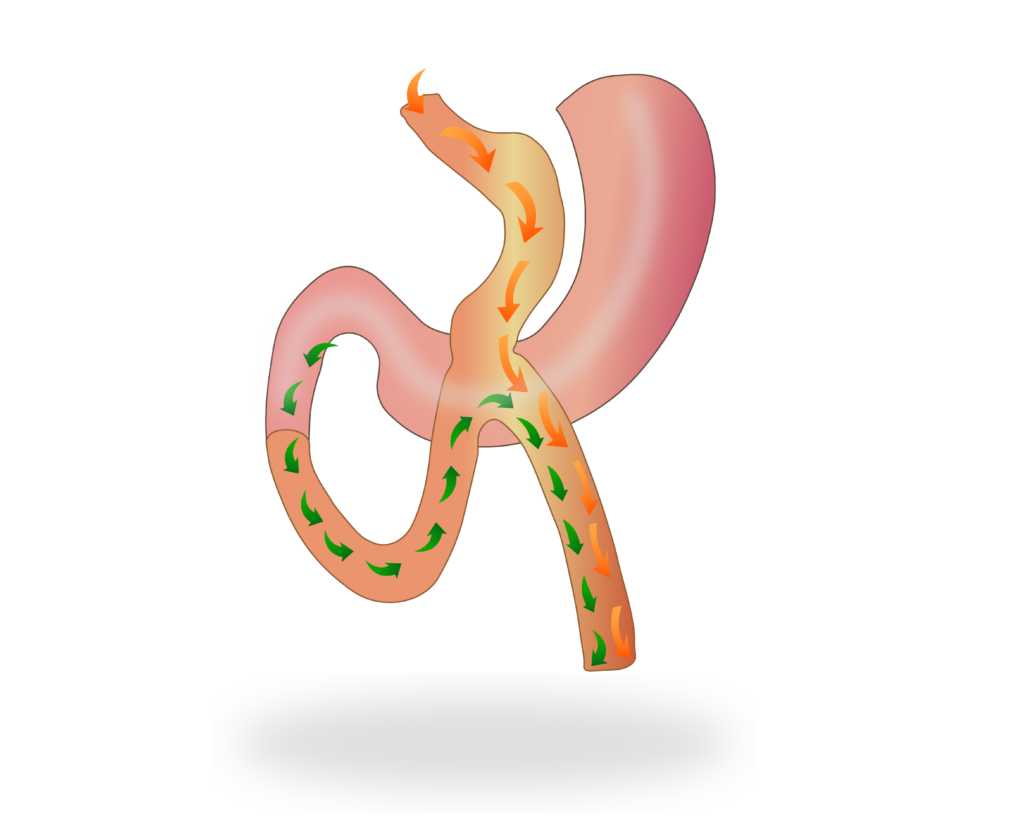
Mini Gastric Bypass surgery is aims to reduce the stomach in half and make a new route for half of the small intestines underneath. It is also strongly effective on Type 2 Diabetes, high blood pressure and hyperlipidemia. Mini Gastric Bypass is a frequently preferred method due to its successful results especially in elderly patients.
Gastric bypasses are malabsorptive bariatric surgical procedures. The aim of gastric bypasses are reducing the stomach volume and separating the small intestines from absorption function. There is different kind of gastric bypasses which has been applied for decades. These are surgeries performed with laparoscopic method.
Mini Gastric Bypass surgery is aims to reduce the stomach in half and make a new route for half of the small intestines underneath. It is also strongly effective on Type 2 Diabetes, high blood pressure and hyperlipidemia. Mini Gastric Bypass is a frequently preferred method due to its successful results especially in elderly patients.
How is Mini Gastric Bypass Performed?
Stages of Mini Gastric Bypass surgery are;
Surgical tools reach into abdominal space under laparoscopic vision from incisions. Half of stomach is seperated with special stapling devices. Separated stomach remains in the abdomen and continues to produce gastric juice.
Second part of the surgery aims to form a new pathway for food, with the half of the small intestines and upper portion of the remaining stomach.
Thus half of the small will not be meeting with the food which reduces calorie absorption almost into half. Digestive juices travels thru first part of the small intestine, then meets with food at the second part of it.These brings the advantage of weight loss.
Roux- en Y Gastric Bypass
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass aims to reduce the size of stomach about 10%. A new pathway for food is formed under reduced stomach via connecting the small intestines. Bypassing the small intestines brings the advantage of calorie malabsorption and reduced stomach works for portion control. It is an effective method for elderly patients with chronic diseases.
Who is a candidate for Gastric Bypass Surgery?
Like other bariatric surgery operations, gastric bypass is recommended for people with severe obesity. Especially elderly patients which has chronicle illnesses related with obesity, including type 2 diabetes, hypertension, obstructive sleep apnea, and GERD (chronic acid reflux) can be a candidate for gastric bypasses.
How Common Is Gastric Bypass Surgery?
Gastric bypasses studied and refined for over 100 years. Gastric bypass surgery was once the most common weight loss surgery, but in recent years it has been replaced by gastric sleeve surgery. Today, gastric bypass accounts for approximately 20% of all bariatric surgeries.
Is Gastric Bypass a Serious Surgery?
Although considered a safe procedure compared to many other common surgeries, gastric bypass is a major operation that will change the digestive system. Even after recovery, it requires special care for the rest of life.
SADI-S Surgery
Duodenal switch and biliopancreatic diversion surgeries are surgical methods that have been performed for a long time. Their metabolic and weight loss effects are strong. In SADI-S only a single anastomosis is performed, this is the main difference than standard Duodenal Switch. Single anastomosis brings less risks.
How Does SADI-S Surgery Work?
In this method, the stomach is first turned into a tube shape. Then, the last 250 centimeters of the small intestine; which is approximately 6.5 meters long, is connected to the last portion of the stomach. SADI- S aims to bypass the absorption of from the rest of the small intesine. Food travels through the stomach and being absorbed in a 250 cm part of small intestine, it is transmitted to the large intestine. Thus, calorie and fat intake is reduced by preventing the absorption.
SADI-S reduces food absorption, and regulates GLP-1 hormone, which stimulates the satiety center, is triggered from the small intestine. Which lowers the appetite.
Therefore, SADI-S surgery is also a malabsorptive procedure, rather than restrictive. SADI-S surgery also increases the insulin production capacity of the pancreas and eliminates the body’s insulin resistance, similar to Duodenal switch and ileal interposition surgeries, which are other examples of metabolic surgery.
What should be taken into consideration after SADI-S surgery?
The gastric sleeve made in SADI-S surgery is slightly wider than the standard sleeve gastrectomy. Therefore, the volume restriction is not as much as in the sleeve gastrectomy. After SADI-S surgery, a special nutrition plan is recommended to prevent carbohydrate rich food intake.
What is Transit Bipartition?
Transit Bipartition is a metabolic surgery method which developed for treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. Aim of this surgery is to make an alternative route for food to travel and meet with digestive juices. In this way, diabetes is controlled by stimulating small intestine hormones.


